
Play narration:
SYMPTOMS OF BACTERIAL DISEASES
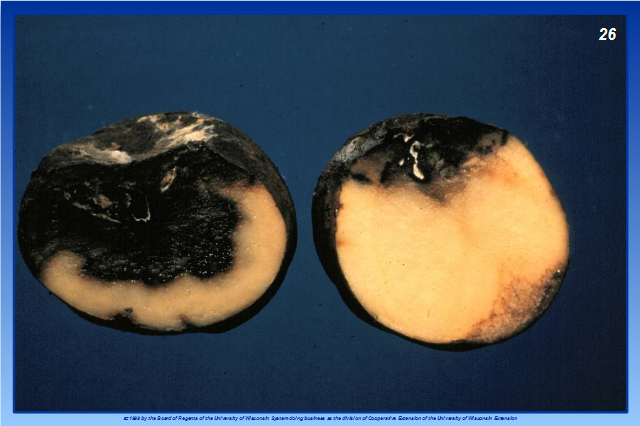
Like fungi, bacteria can cause ROTS and soft rot of potato (shown in this photo) is a classic example. The bacterium that causes this disease, Erwinia carotovora, produces an enzyme that degrades pectin, the substance that serves as the "glue" that holds plant cells together. Once pectin is degraded, the potato tuber becomes a squishy, disgusting mess. Interestingly, the foul smell that people typically associate with rotted potatoes is not due to Erwinia carotovora. The chemicals that give rotten potatoes their awful smell are produced by other bacteria that invade the rotted tissue after the pathogen has done its work.